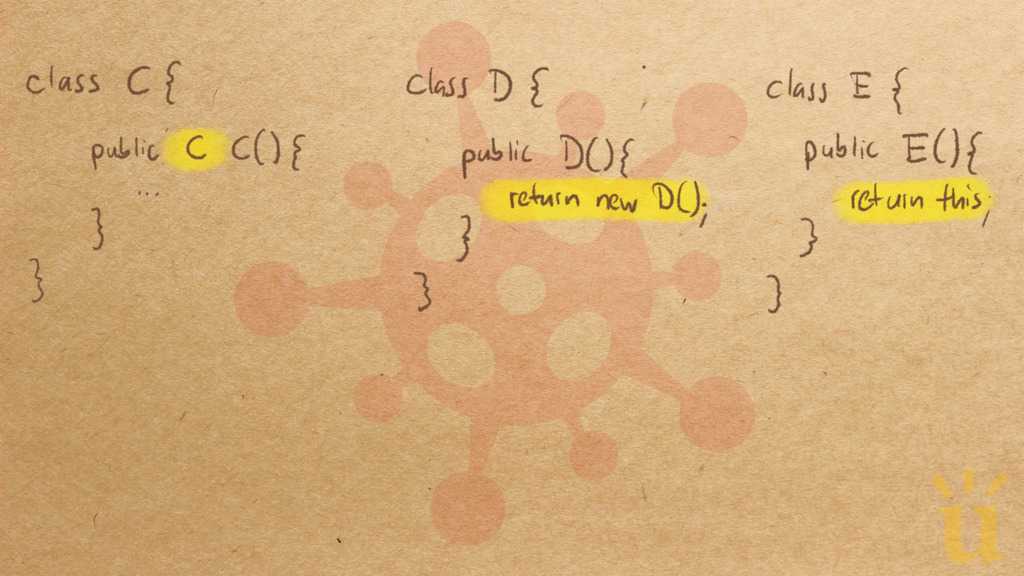
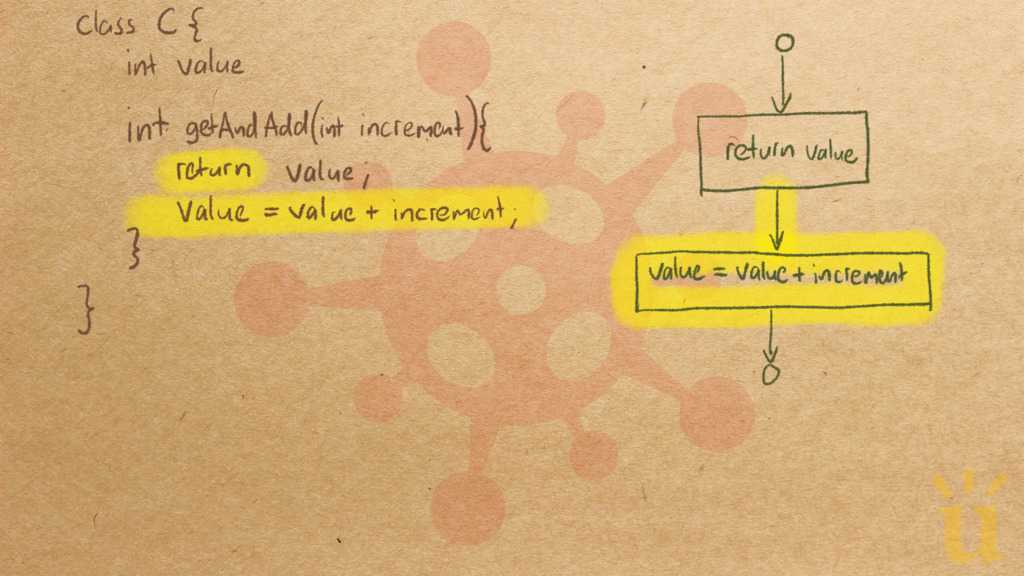
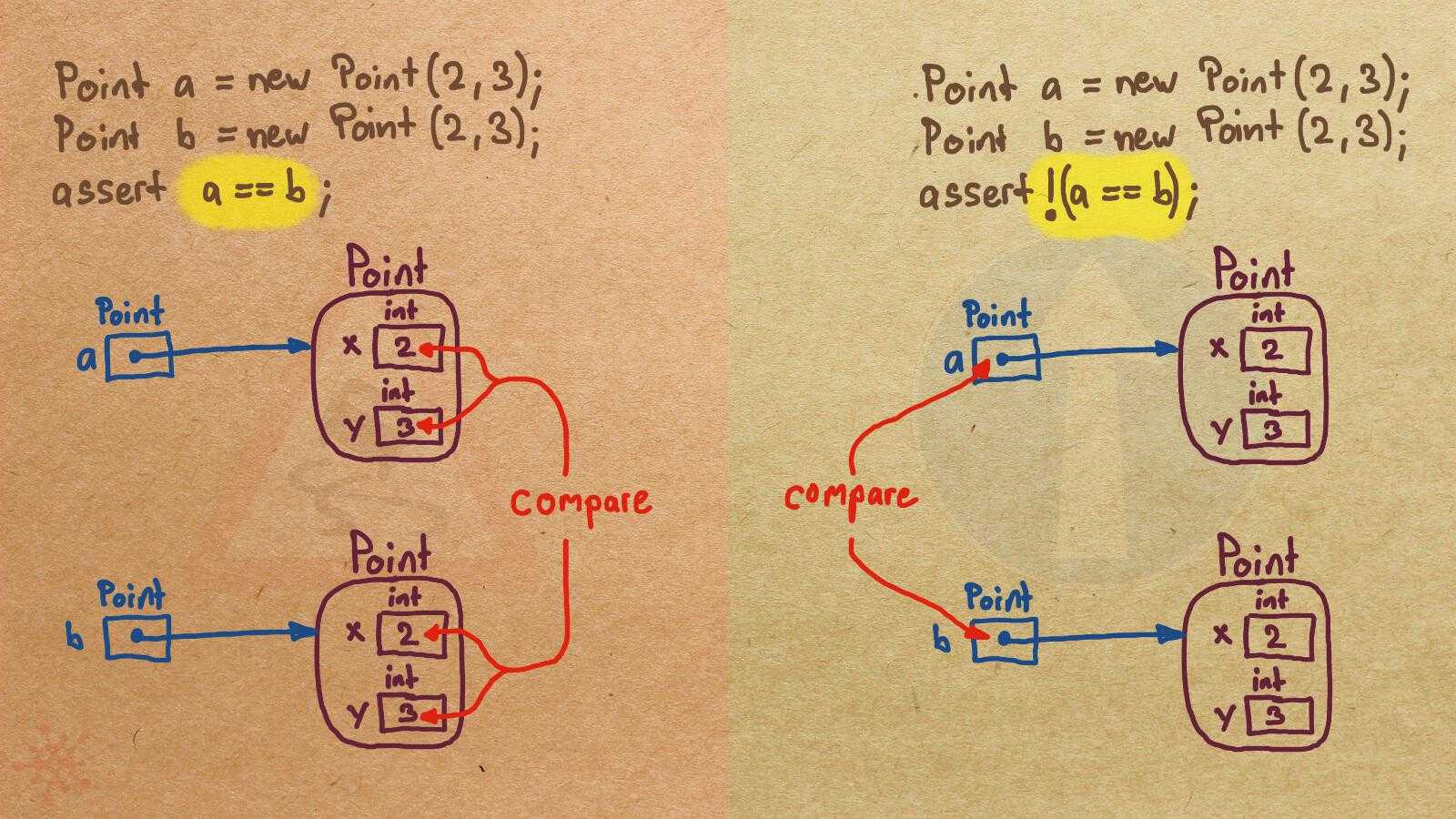
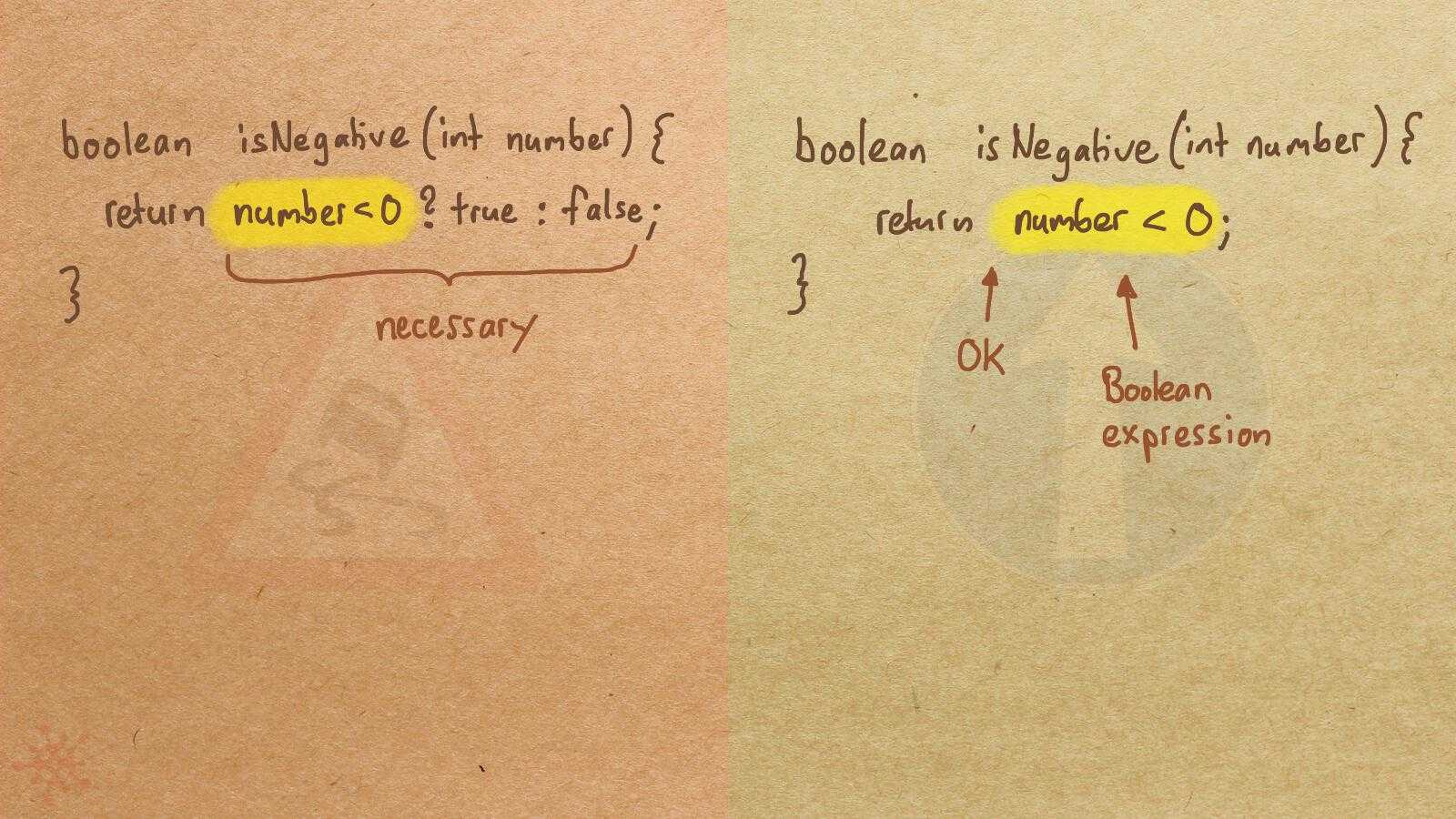
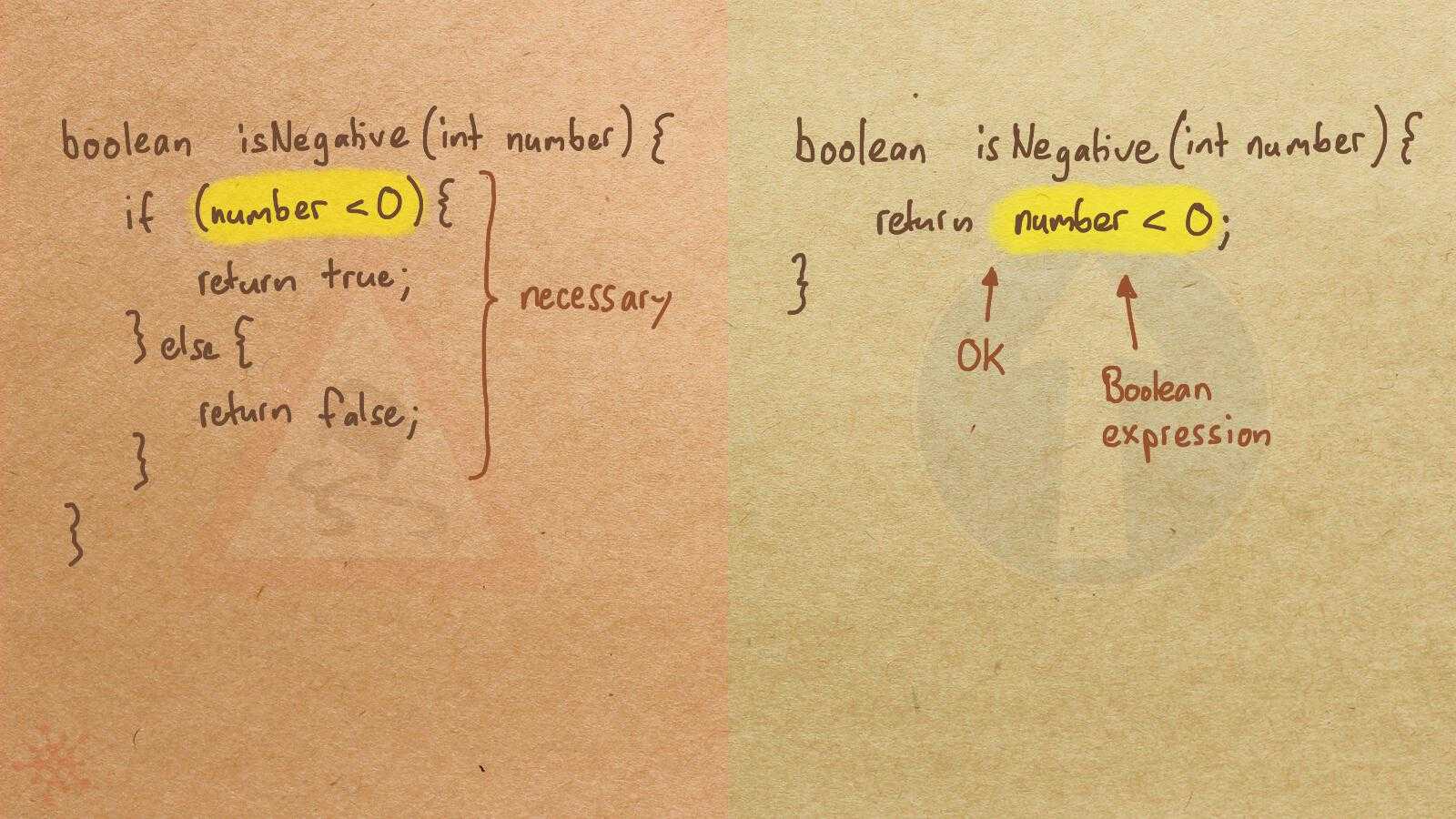
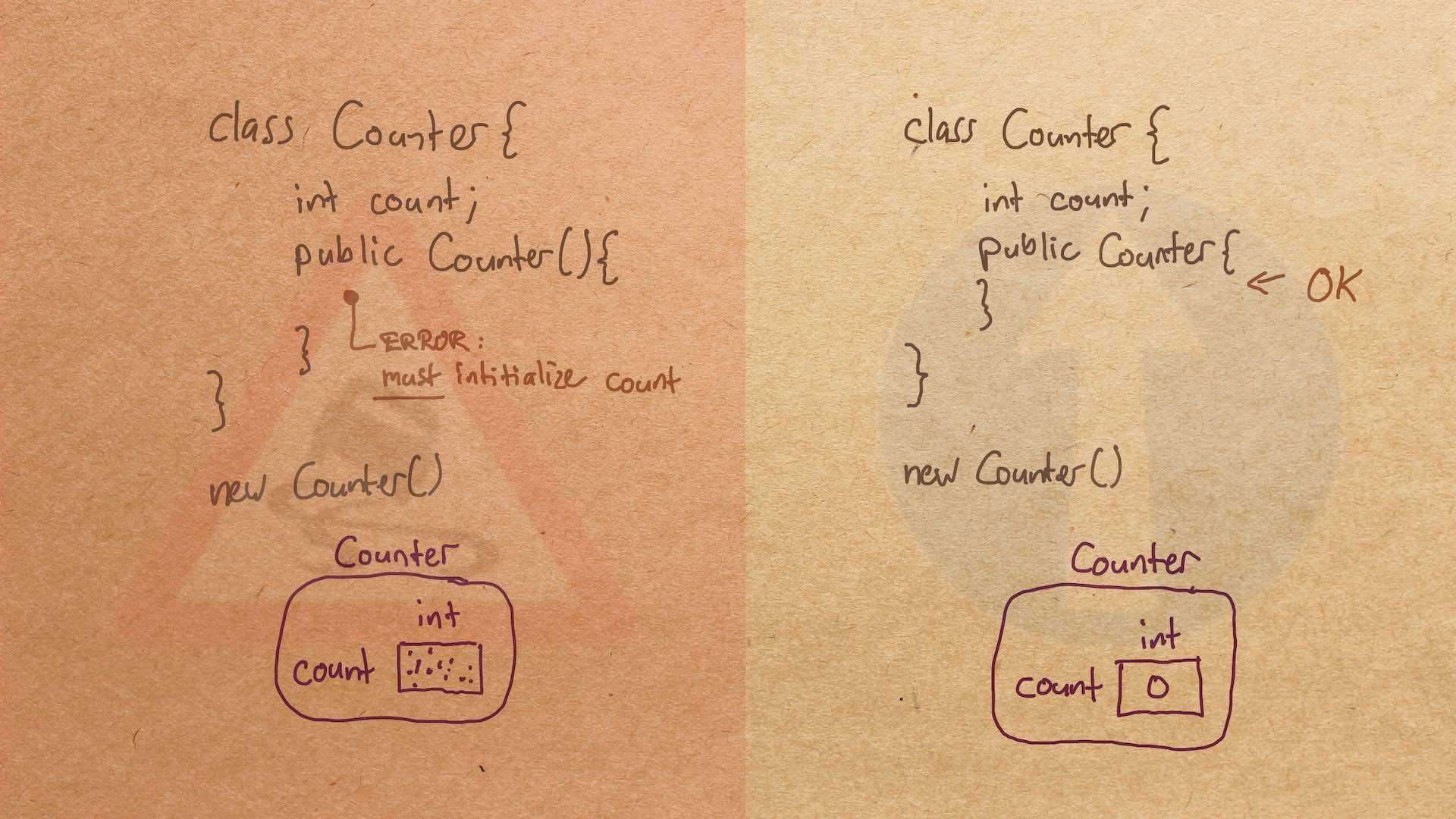
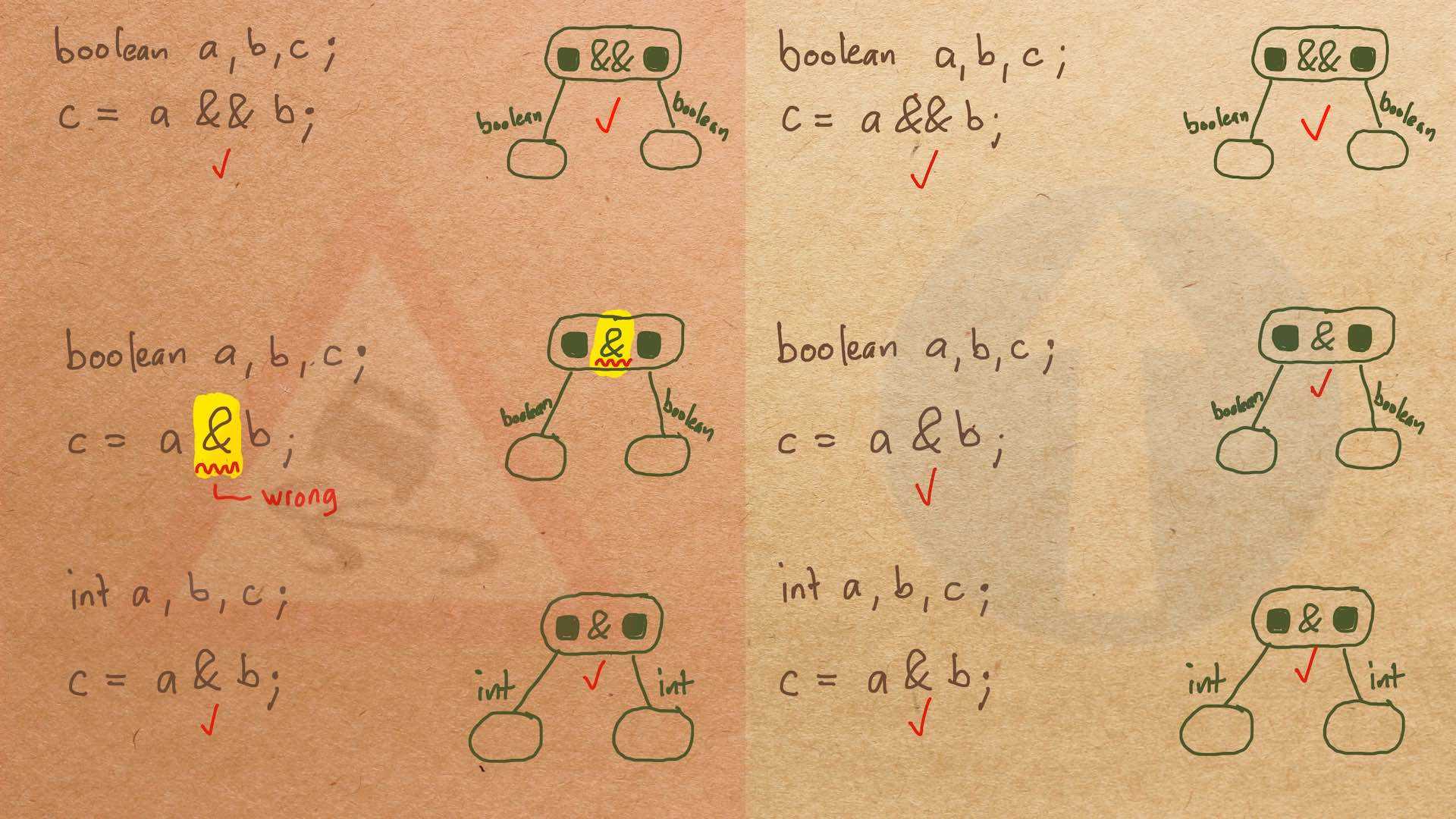
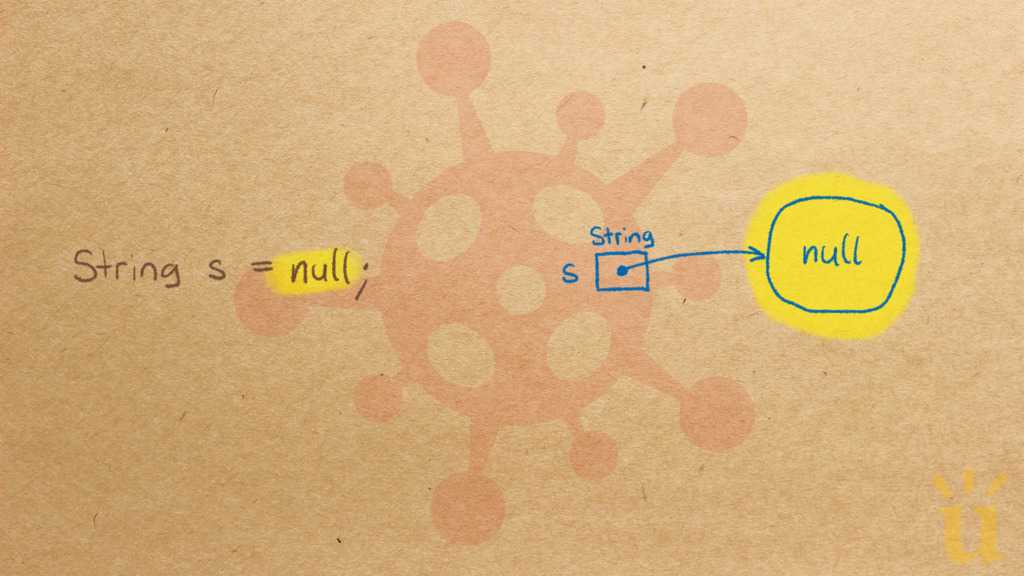
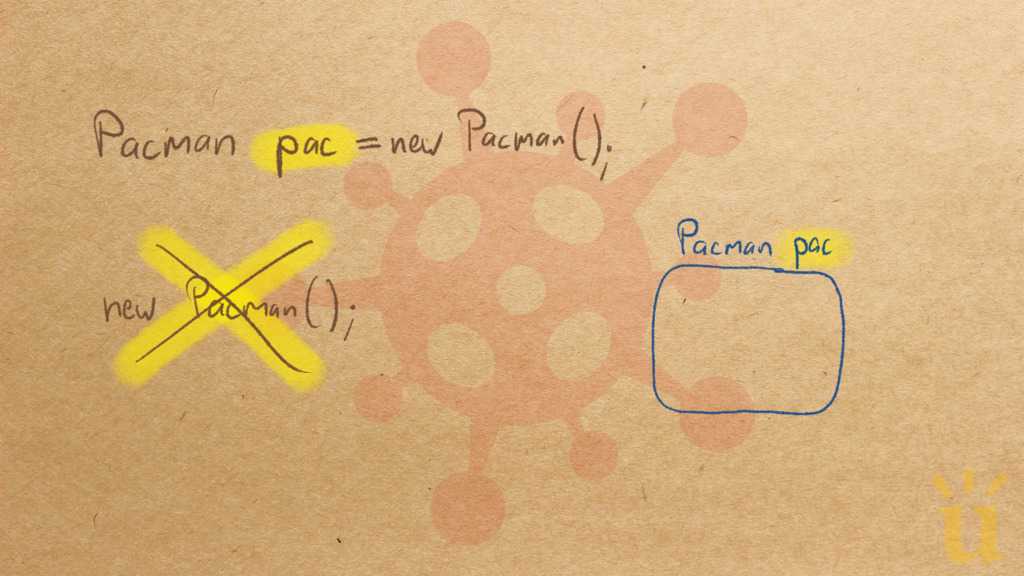
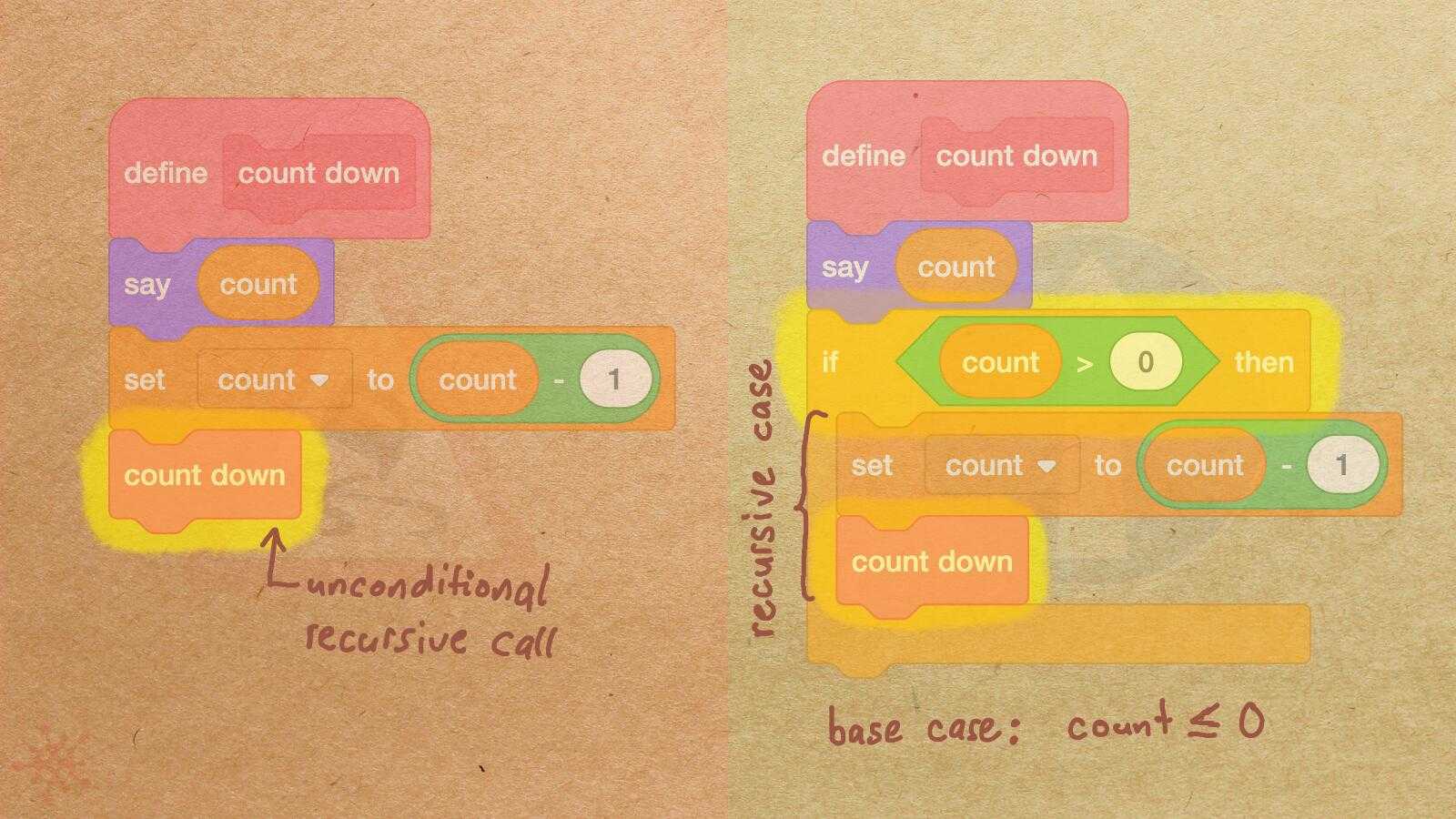
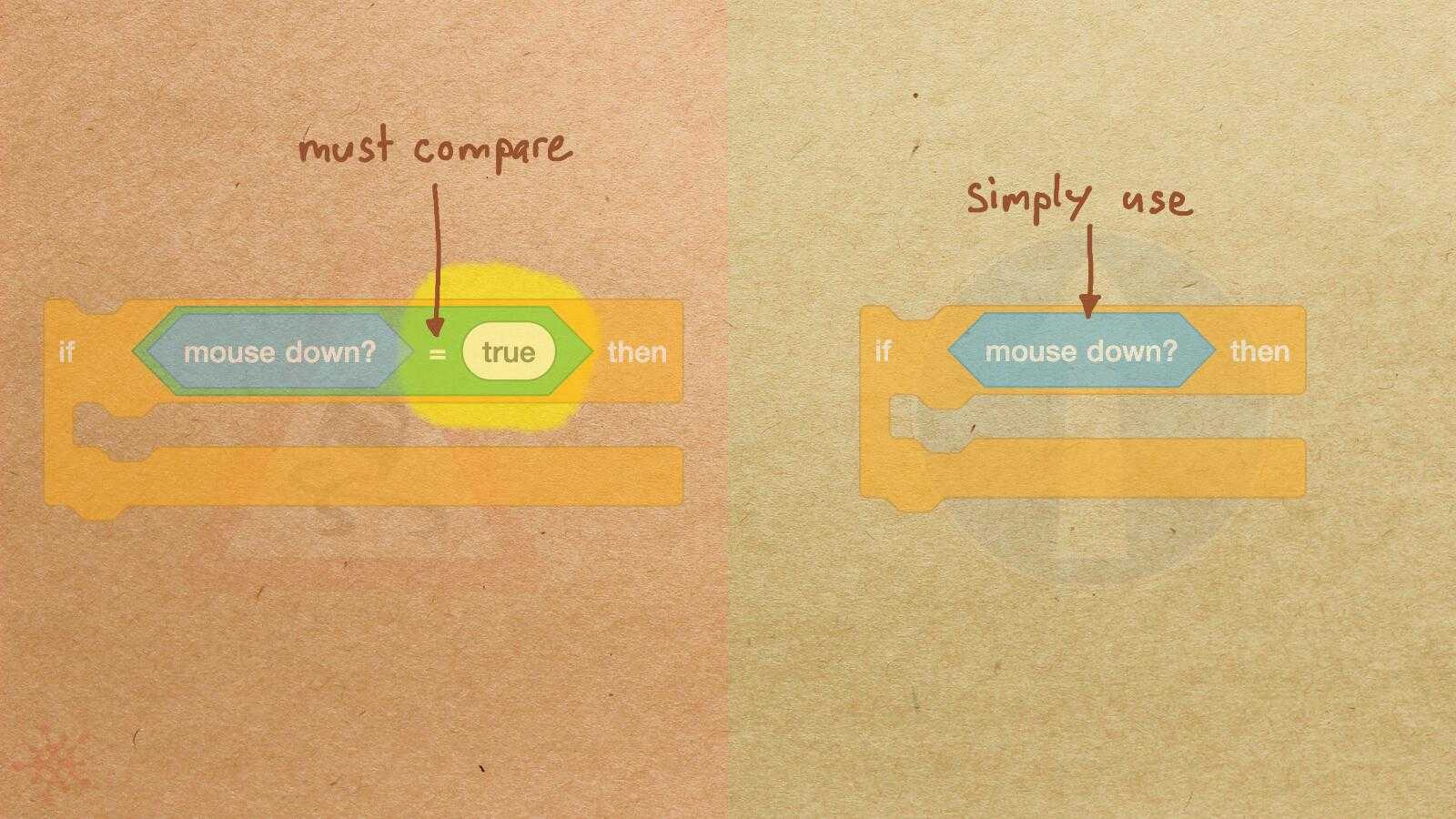
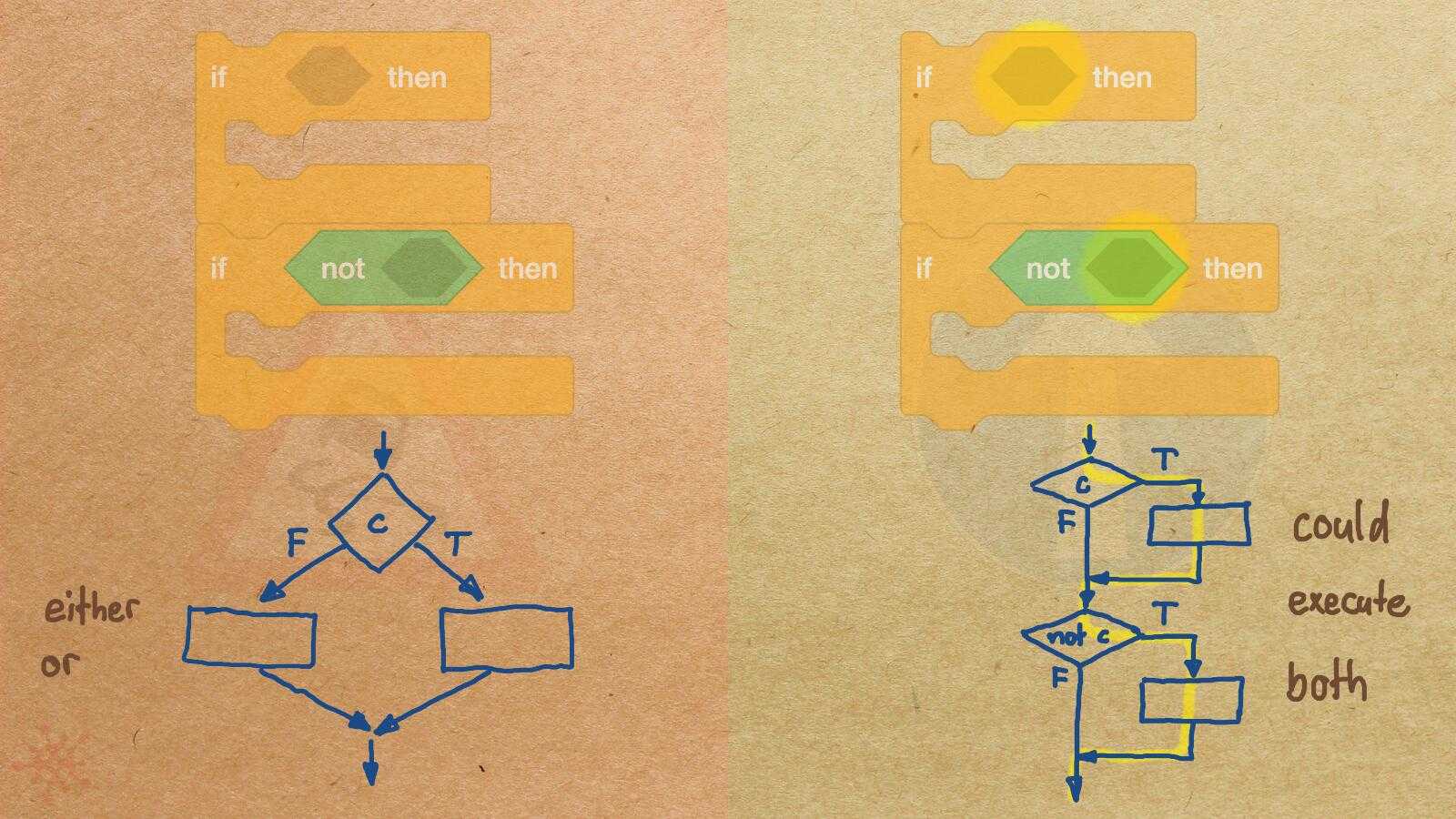
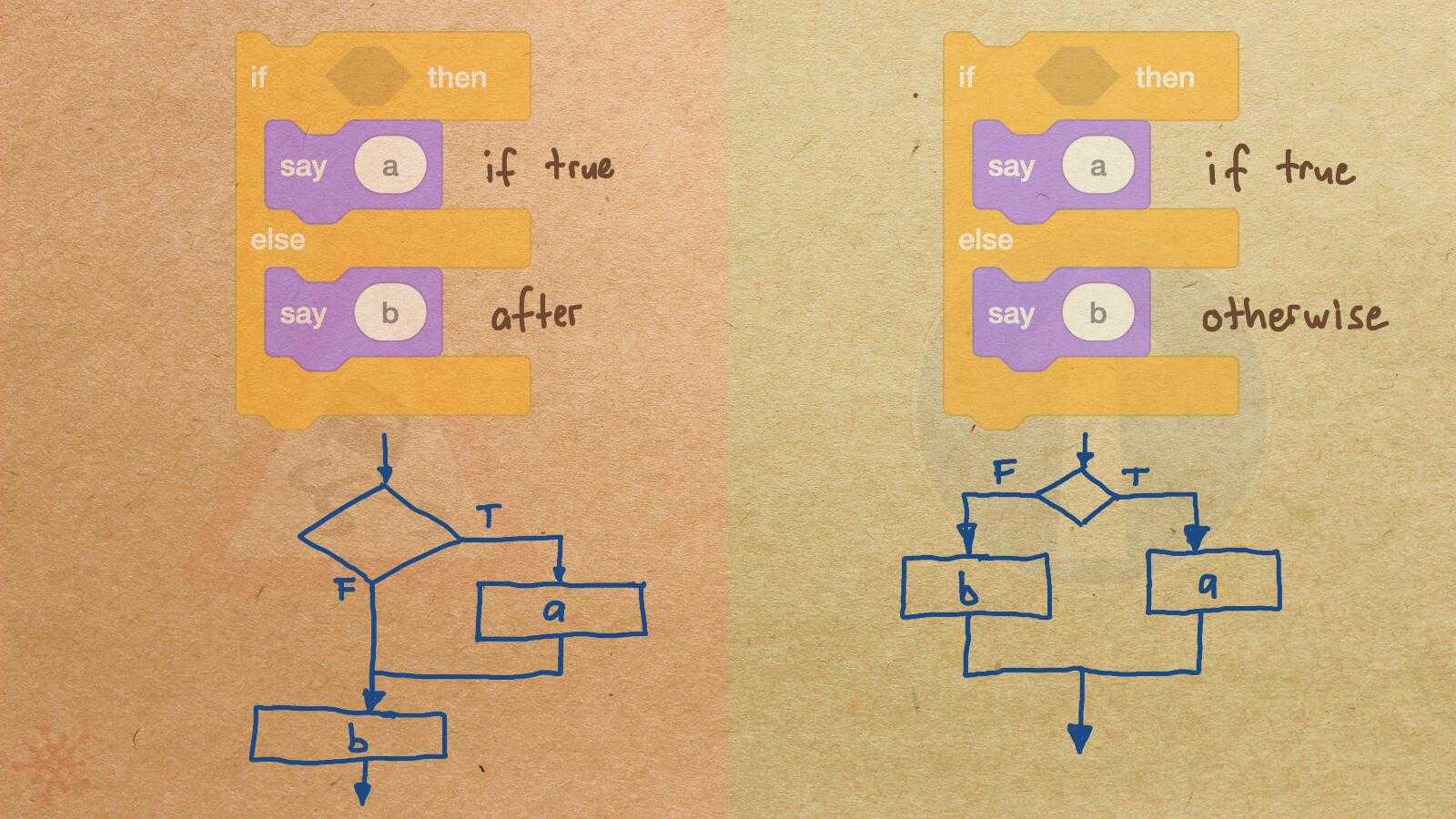
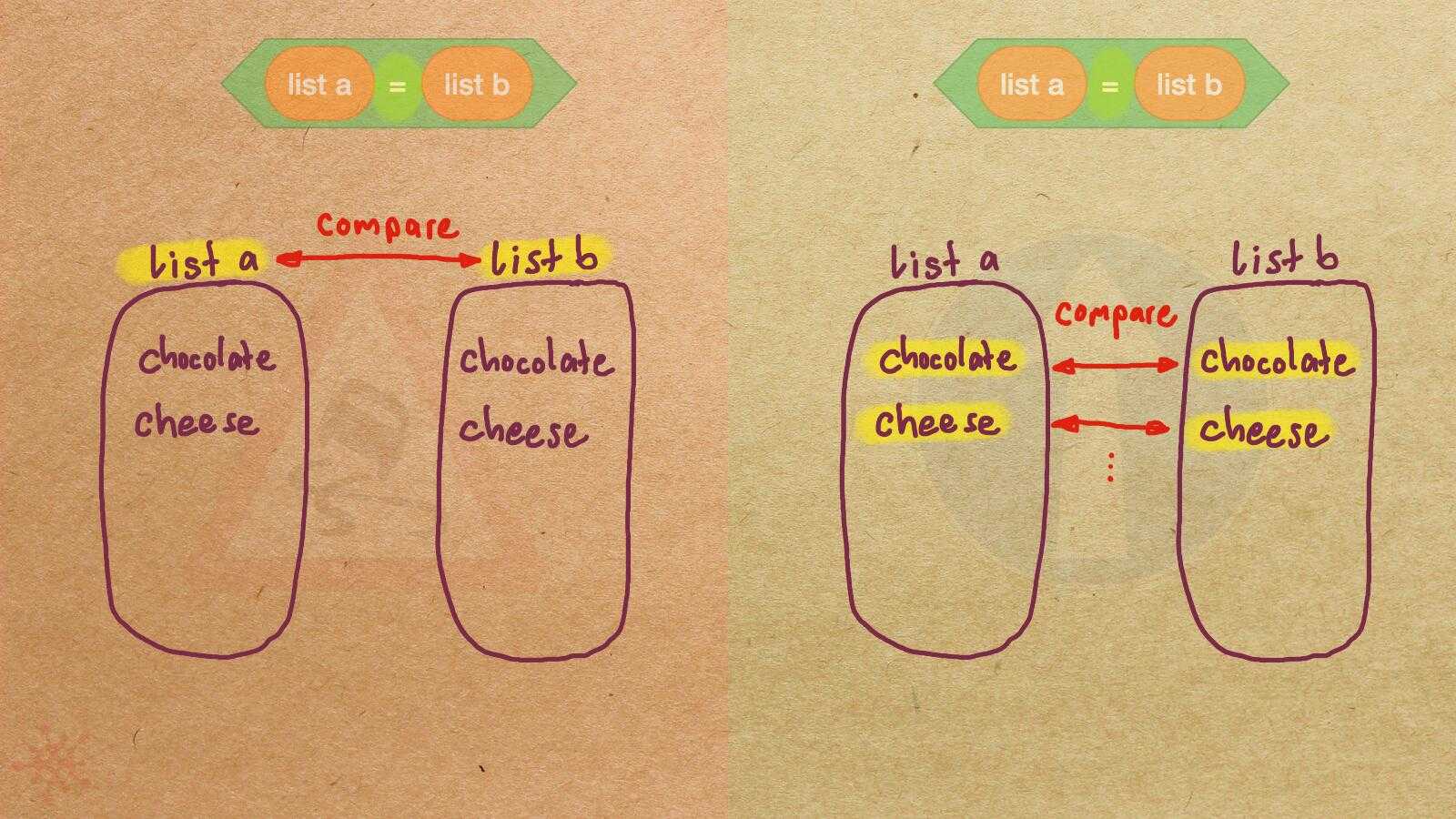
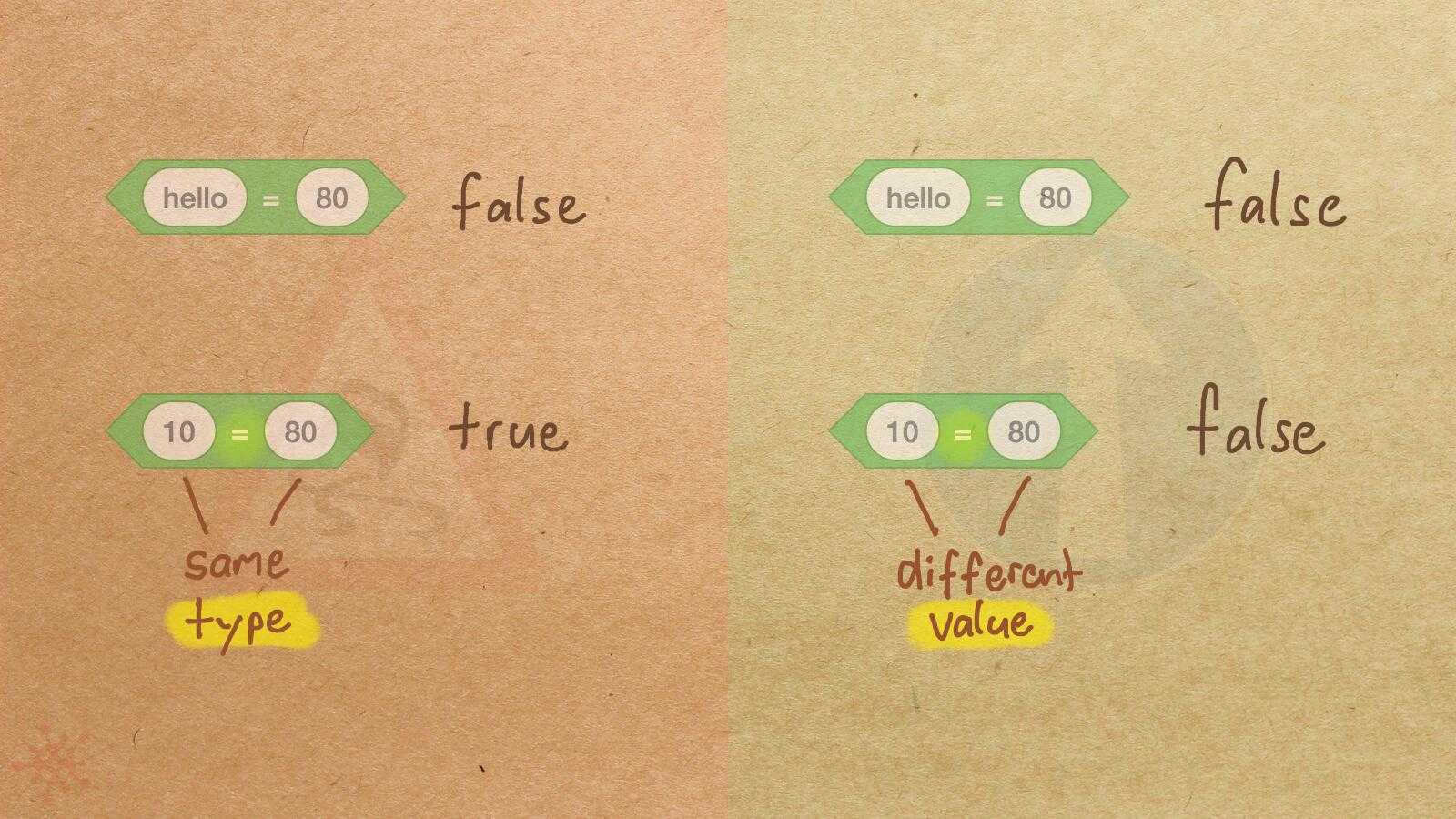
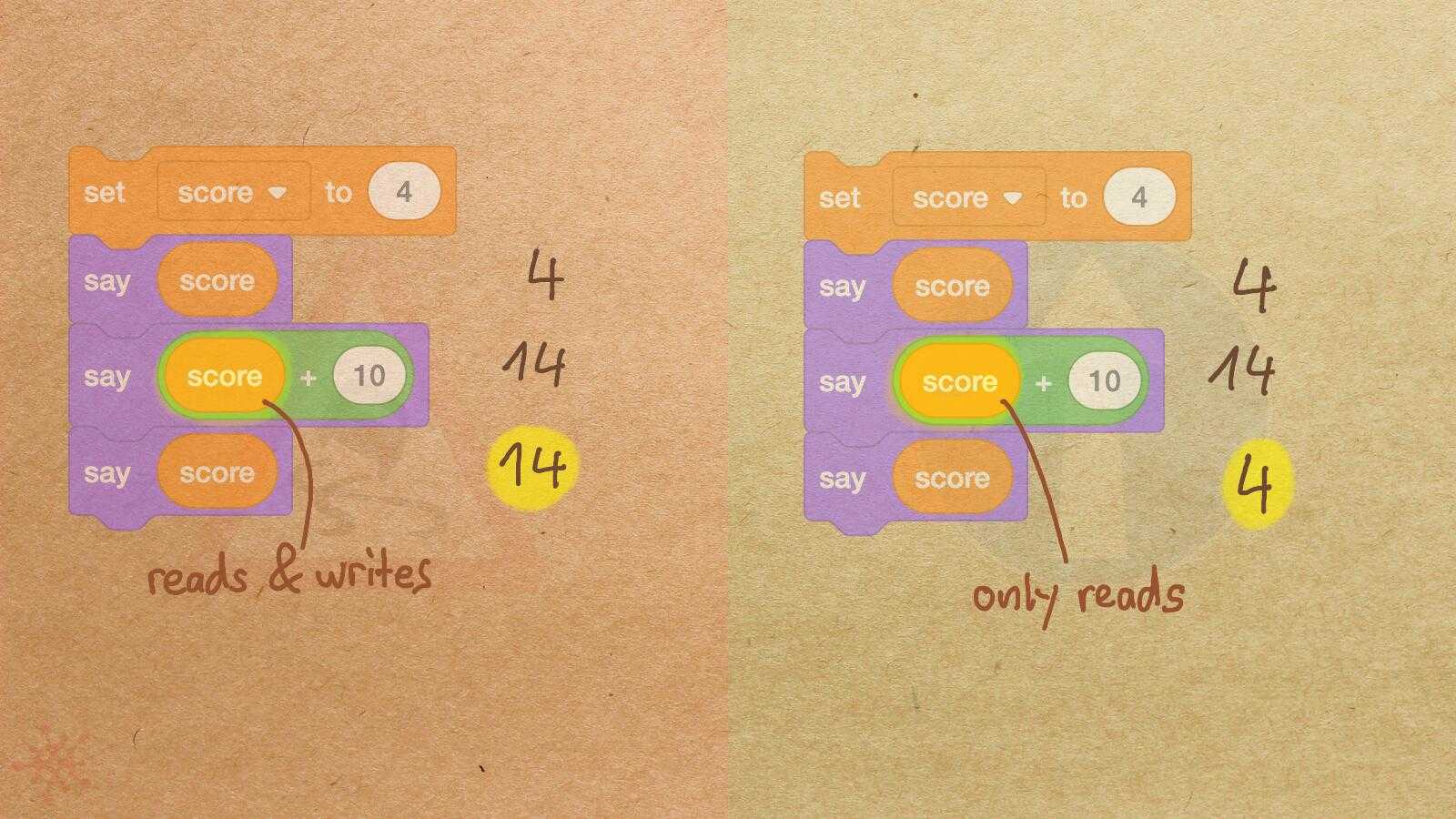
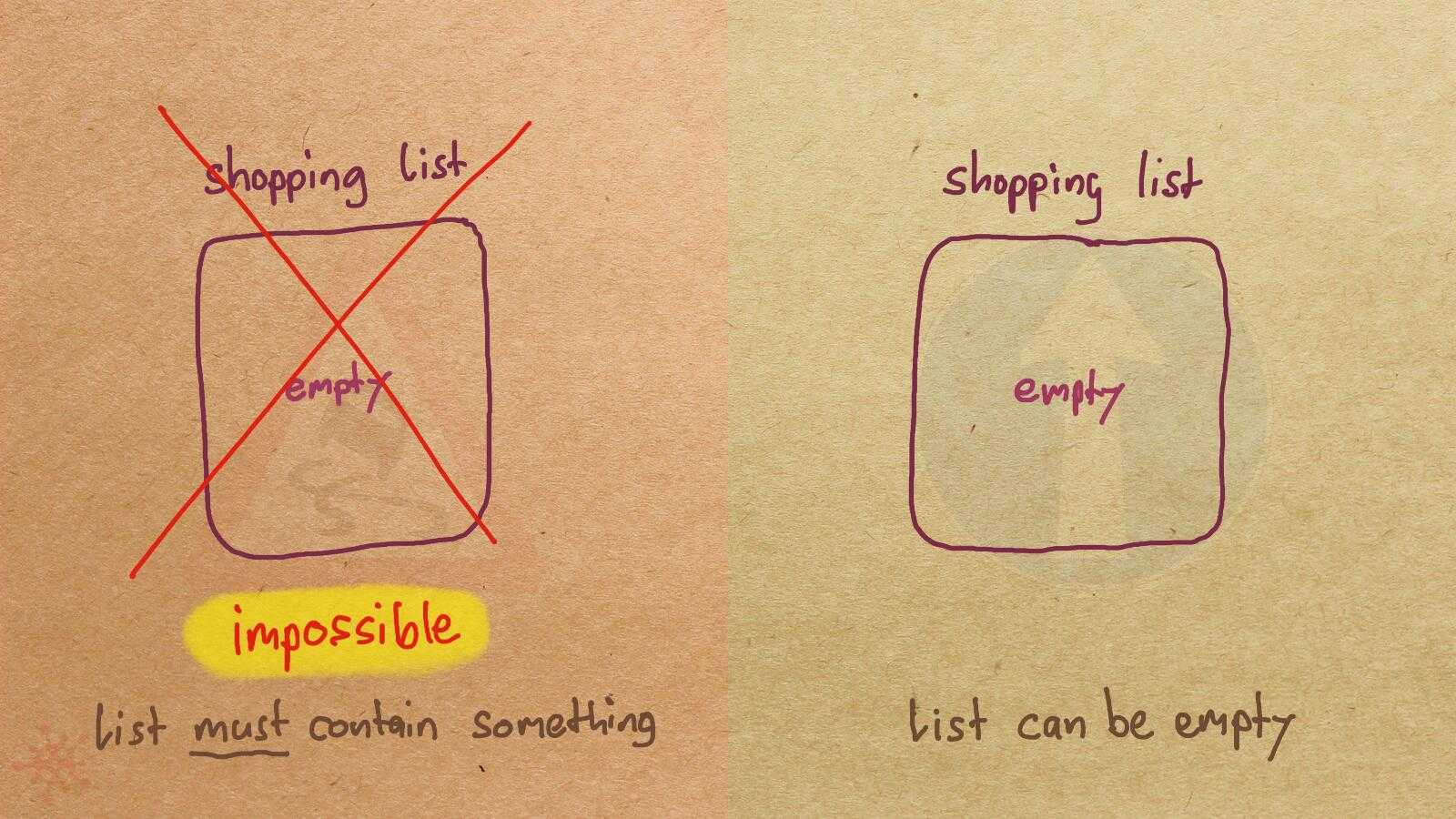
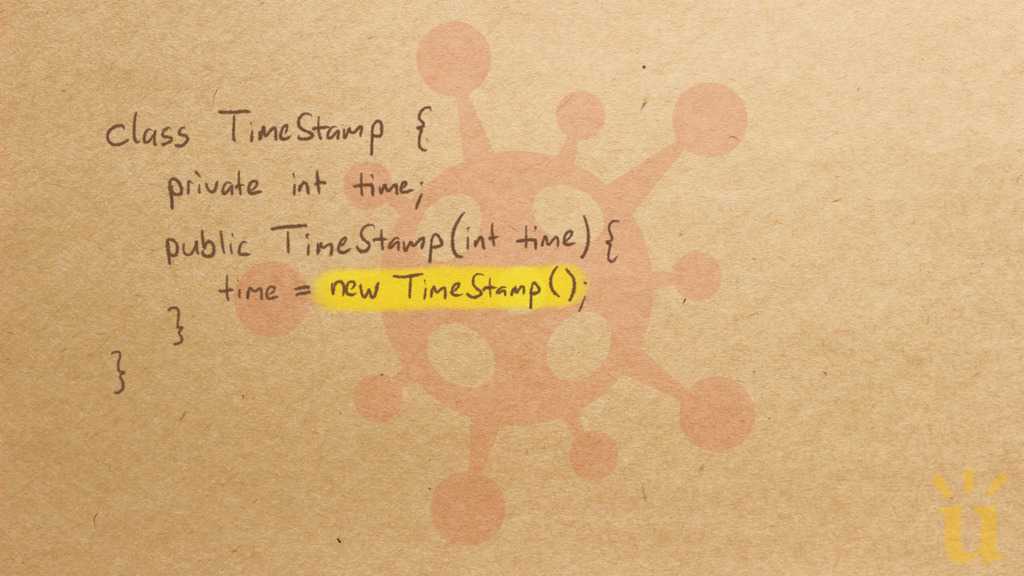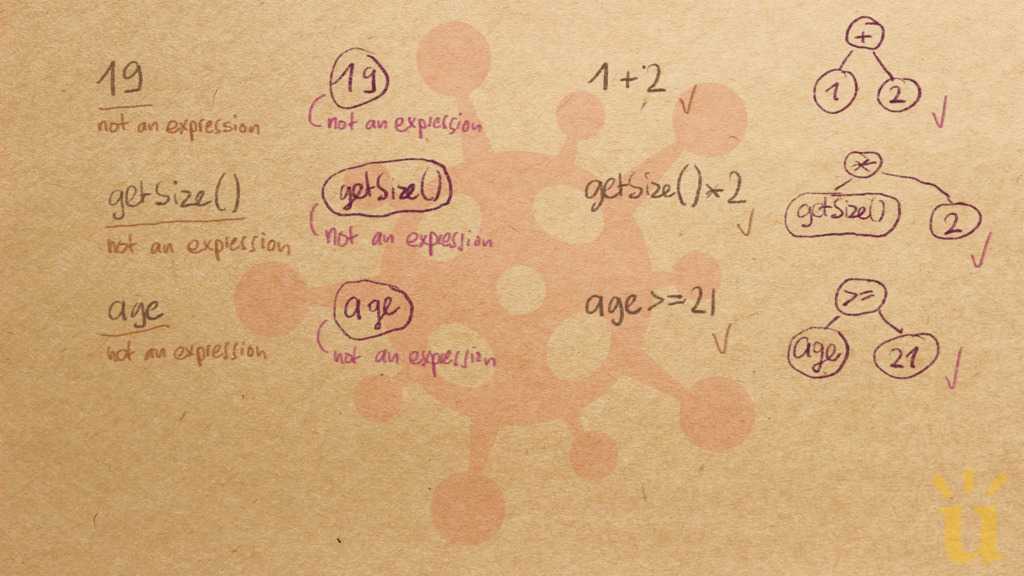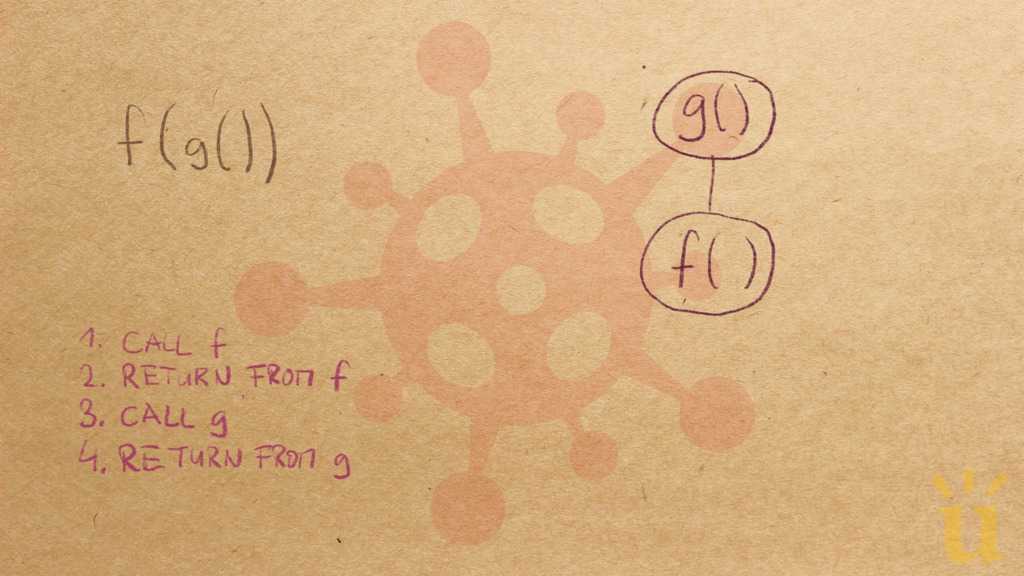Misconception Count Does Not Imply Language Difficulty
There is no connection between the number of misconceptions listed here and the difficulty of the corresponding programming language. The effort we spent on collecting misconceptions is very different for different languages. It would be inappropriate to reason about the quality of languages based on the number of misconceptions in this collection.